Harnessing the Power of Workforce Planning for Strategic Success

Workforce planning is a crucial tool for maintaining a competitive edge in 2025. Organizations must align their workforce strategies with evolving market demands and technological advancements to thrive.
According to Gartner's "Top 5 HR Trends and Priorities Report," only 15% of companies engage in strategic planning of their workforce. Without appropriate workforce strategies, you can leave a serious gap in your ability to align talent with long-term business goals, stunting the effectiveness of human resources (HR) teams.
By setting a concrete plan, you can reduce inefficiencies, optimize costs, and build a workforce that is prepared to meet both current and future challenges.
What is workforce planning?
Workforce planning is the process of analyzing, forecasting, and planning workforce supply and demand to ensure an organization has the right people, with the right skills, in the right roles, at the right time. It involves assessing current workforce capabilities, predicting future needs, and developing strategies to fill gaps—whether through hiring, training, succession planning, or workforce optimization.
Analyzing your current workforce at the organizational and operational levels allows you to effectively assess future requirements and prepare for inevitable changes such as retirements, turnover, or industry disruptions.
A strategic workforce plan involves analyzing the quantity, skills, and mix of talent within your organization in order to proactively align your organization’s current business needs and future goals.
Reliable data and predictive analytics are vital to accurately address gaps in staffing and optimize your team’s potential. Tools like Workhuman® IQ offer unparalleled views of people dynamics, cultural health, program performance, skills, and more.
A solid workforce strategy delivers measurable benefits that help drive an organization’s competitiveness and sustainability:
- Targeting inefficiencies: By identifying redundancies or resource gaps, you can optimize workflows and align talent to meet business needs.
- Reducing labor costs: Strategic planning reduces the likelihood of overstaffing or understaffing, leading to better financial management. According to a report by NCSES on labor costs in the USAOpens in a new tab, labor costs account for over two-thirds of total business R&D performance, so optimizing these costs is essential.
- Identifying talent development opportunities: Uncover skill gaps and enable targeted training programs, upskilling employees to meet future needs. The Skills Accelerators Network, an initiative of the World Economic Forum, predicts that 50% of all employees will require reskilling by 2025 due to technological advancements.
- Improving employee retention and productivity: A well-planned workforce strategy creates clear career paths, boosts employee morale, and reduces turnover. This often results in increased productivity.
- Preparing for workforce changes: Workforce preparedness enables organizations to remain agile and adapt to workforce changes. Retirements, talent shortages, or economic shifts all happen without disrupting operations.

This proactive approach means your workforce will evolve alongside your strategic goals, positioning your organization for long-term success.
Understanding the basics of workforce planning
Get to know the fundamentals that will propel you into becoming a strategic workforce planning master.
The role of data analytics in workforce planning
With the rise of data analytics and artificial intelligence, it's never been easier to use raw workforce data to make tangible improvements in your organization. By tracking important metrics and leveraging technology, you can anticipate talent needs, analyze trends, and make informed decisions.
The following metrics are central to a workforce plan:
- Workforce demand forecasting: Predicts the number of employees needed to meet future business requirements
- Workforce supply analysis: Examines the current workforce and assesses gaps in skills, roles, or capacity
- Turnover and retention rates: Identifies patterns of attrition and factors driving employee exits, helping reduce turnover
- Time-to-hire and cost-per-hire: Tracks recruitment efficiency, showing how quickly and cost-effectively roles are filled
- Skills and competency gaps: Highlights gaps between existing workforce skills and those required for future goals, informing training initiatives
- Productivity metrics: Measures workforce efficiency by assessing outputs relative to inputs, allowing for targeted improvement
For example, a company may analyze high turnover rates in a specific department and identify underlying issues, such as workload imbalances or a lack of career growth opportunities. With this information, leadership can address the root causes and improve retention. Being data-driven empowers you to optimize staffing, minimize disruptions, and aim for organizational success.
Key elements of the workforce planning framework
Successful workforce planning begins with identifying evolving workforce needs. Do this by engaging leadership and stakeholders and gathering internal data on your workforce through analytics tools.
Integrating workforce planning with business strategy and financial strategies ensures alignment with operational goals and long-term growth. Monitoring external labor market trends, such as talent availability, emerging skills, and industry challenges, also helps organizations adapt proactively.
Additionally, building your HR team’s capability to analyze and interpret talent data using talent intelligence tools such as predictive analytics and dashboards enables better decision-making and helps you identify workforce gaps.
Examples of workforce planning across varying industries
Many organizations across industries have successfully implemented workforce planning strategies. Two impactful examples include:
Healthcare sector – Kaiser Permanente
Kaiser Permanente, one of the largest integrated healthcare systems in the U.S., identified a looming nursing shortage using workforce analytics. They proactively developed a comprehensive workforce strategy, including recruitment initiatives, better employee retention programs, and partnering with nursing schools to develop future talent pipelines.
As a result, they reduced workforce shortages and improved patient care outcomes.
Retail sector – Walmart
Retail is especially known for cyclic peaks and troughs when it comes to staff requirements. Shifts in buying behaviors and seasonal demands, especially during peak shopping periods like Black Friday and the holiday season, can be challenging.
Through data-driven planning, Walmart optimizes its hiring processes and staffing models to ensure sufficient labor coverage while minimizing excess costs. Their strategy includes predictive talent analytics to determine staffing levels across stores and distribution centers.
This approach has enhanced both customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Walmart's example highlights how a retail company can assess staff growth, identify improvement areas, and plan for succession through data-driven strategies:
- Assessing staff growth: Using predictive analytics, Walmart evaluates staffing needs across stores and distribution centers. This data helps measure growth trends, ensuring staffing levels align with demand during peak seasons and identifying whether teams are expanding or stagnating.
- Identifying areas for improvement: The ability to predict cyclic demands reveals gaps in labor coverage, operational inefficiencies, or hiring delays. This insight allows managers to refine recruitment, training, and workforce allocation to minimize customer service disruptions and excess labor costs.
- Planning for succession: Walmart’s data-driven approach enables leadership to identify high-potential employees who perform well during peak seasons or under pressure. By tracking performance, Walmart can nurture its top talent, offering opportunities for career advancement and building a pipeline for future leadership roles, ensuring sustainable succession planning.
Companies can adopt similar workforce planning techniques by:
- Leveraging predictive analytics to anticipate future staffing needs
- Investing in employee upskilling initiatives to close skill gaps
- Building robust succession plans to ensure leadership stability
Workforce planning process – The six core steps
There are six core steps to effective workforce planning involving collaboration between HR, department managers, leadership teams, and employees.
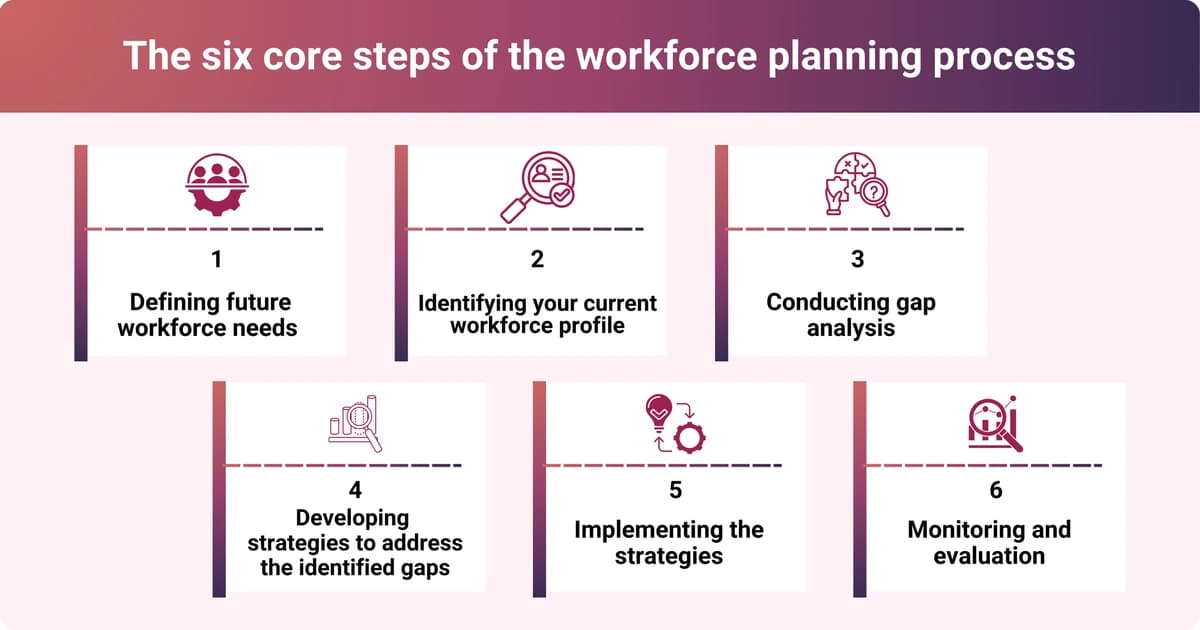
1. Defining future workforce needs and deciding on a strategic direction and goals
Step one is to work together with key stakeholders and senior executives across departments and HR to identify future workforce needs based on business goals. This provides a roadmap for aligning your workforce with organizational objectives and ensuring sustainable growth.
By understanding specific requirements for talent and defining exactly what you want to measure, you can identify key milestones and outline performance metrics. For example, a company expanding into a new market might implement effective recruitment strategies for skilled roles such as sales and operations managers to meet future demand.
2. Identifying your current workforce profile
It is essential to analyze your existing workforce and create a comprehensive workforce profile. This involves assessing both the quality and quantity of employees:
- Quantity: Evaluate the number of employees in each department, their roles, and headcount trends. Workforce management software can track metrics like headcount, turnover rates, and vacancy rates.
- Quality: Assess employee skills, qualifications, and experience to determine if the current workforce aligns with future organizational needs. Performance reviews, skills assessments, and feedback from managers can identify top performers and areas requiring development.
Combining quantitative and qualitative data delivers insight into your strengths and weaknesses.
3. Conducting gap analysis to identify potential gaps
Perform a gap analysis to identify differences in the current workforce profile and future workforce requirements. By comparing employee skills, experience, and qualifications with organizational needs, businesses can identify areas with skill shortages, surpluses, or other gaps. Consider:
- Skills gaps: Analyze whether employees possess the necessary skills to meet future demands and identify skills you can upskill existing employees in
- Workforce surpluses: Identify areas where staffing levels exceed current needs, leading to inefficiencies or unnecessary costs
- Retirements and attrition: Assess the potential impact of any upcoming retirements, resignations, or turnover, creating critical skill gaps
These analyses pinpoint your workforce challenges, allowing informed decisions about recruitment, reskilling, and succession planning.
4. Developing strategies to address the identified gaps
Once you have identified gaps, develop targeted strategies to address them. Align the overall business strategy with workforce realities to create a practical plan for the future. You can incorporate OKRs at this point, defining the objectives and key results to aim for with strategies such as:
- Hiring new talent: Recruiting skilled professionals to address immediate and future gaps
- Reskilling or upskilling: Providing training programs to equip existing employees with in-demand skills
- Workforce redeployment: Realigning employees to roles that better match their strengths and organizational needs

To observe this in action, take a car manufacturer forecasting growth in electric vehicle (EV) production. With an analysis of revenue and growth projections, the manufacturer determines it has greater staffing needs for engineers, battery specialists, and assembly line workers.
By understanding market forecasts and aligning its workforce strategies, the company can plan for future hiring and training.
5. Implementing the strategies
Time for action! The implementation phase translates strategic workforce plans into actionable steps. Successful implementation requires knowing your solutions. They could be:
- Definitions of new roles and responsibilities: Define new roles and responsibilities by clarifying job descriptions, competencies, and expectations for evolving positions. Leverage goal-setting theory to establish specific, measurable, and challenging goals that drive higher performance.
- Data recording and tracking: Use HR technology to record workforce changes, track employee progress, and measure results.
- Effective communication: Communicate the plans to leadership, managers, and employees to ensure transparency and buy-in.
- Measurement criteria: Develop metrics to monitor the success of implementation, such as time-to-hire, employee engagement scores, and training completion rates.
6. Continuous monitoring and evaluation
Iterative in nature, workforce planning is not a one-time process. It requires ongoing monitoring and adjustment. After implementing strategies, organizations must continuously evaluate their effectiveness:
- Tracking progress: Regularly review key performance indicators (KPIs), such as employee retention, productivity rates, and workforce costs.
- Collecting feedback: Gather input from managers and employees to understand challenges or successes. Workhuman’s Conversations® is a tool that combines agile performance development with structured feedback and assessments for continuous communication, ideal for getting feedback.
- Adjusting strategies: Adapt workforce plans to address changing business priorities, labor market trends, or unforeseen challenges.
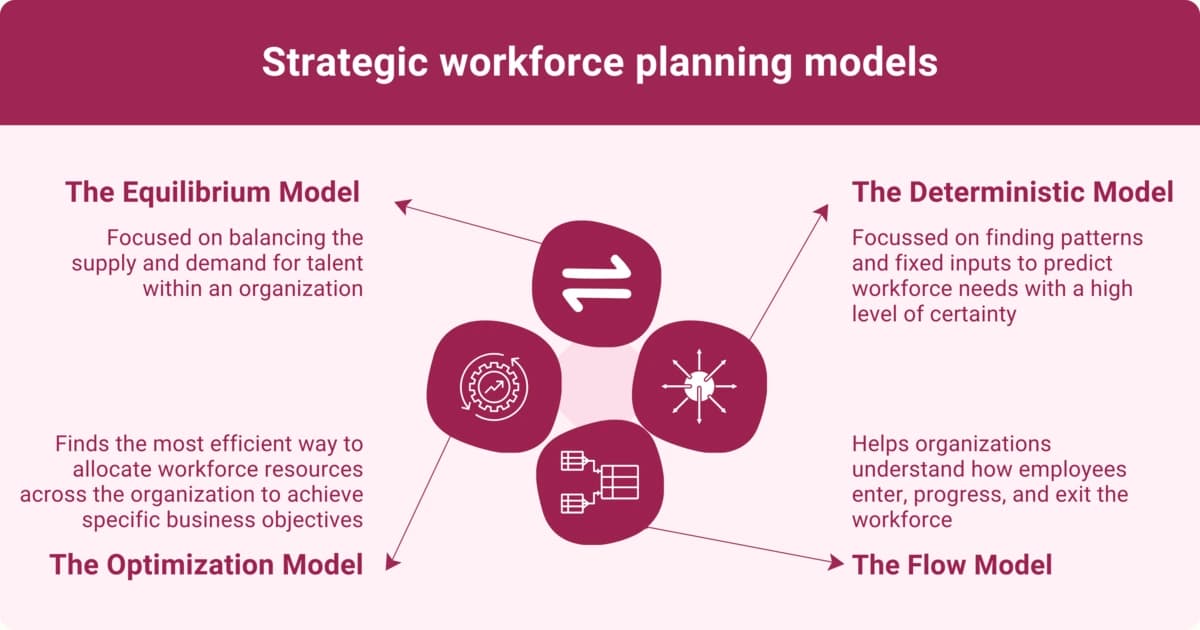
Strategic workforce planning models
Depending on your needs, objectives, and industry, there are four well-versed strategic workforce planning models you should know to start creating a concrete workforce plan.
1. The Equilibrium Model
Focused on balancing the supply and demand for talent within an organization, this model includes supply-and-demand analysis, labor market analysis, and skill gap analysis for long-term forecasting to prevent talent gaps or surpluses. The equilibrium model emphasizes a stable and motivated workforce that supports long-term success.
- Supply side: This involves assessing the internal workforce (e.g., skills inventory, retirements, turnover) and considering external factors like labor market trends and demographic changes.
- Demand side: The model projects future workforce needs based on business growth, market conditions, and technological advancements.
An organization maintains equilibrium by continuously adjusting the workforce composition. This practice works well in industries with relatively predictable demand, such as public services or education, where steady growth and planning are more easily forecasted.
2. The Deterministic Model
A less flexible model, analyzing historical data, can find patterns and fixed inputs to predict workforce needs with a high level of certainty. Although this model does not easily account for uncertainty, trend analysis, fixed ratio, and regression analysis, it can focus on producing accurate resource forecasts.
- Inputs: Factors could include sales projections, historical performance, or operational goals.
- Outputs: Based on inputs, the model generates a workforce forecast, often by determining optimal headcounts for each department or function.
Deterministic workforce planning is particularly useful in businesses that operate in a stable and predictable environment, large manufacturing facilities, or industries with consistent demand patterns.
3. The Flow Model
When it comes to workforce transitions, hiring, promotions, retirements, or terminations, the flow model helps organizations understand how employees enter, progress, and exit the workforce. Markov analysis, career path planning, and succession management can determine career paths, which are used in turn to develop employee growth initiatives to combat high turnover.
- Employee flow: Analyzing how employees move through different roles within the company or across different departments
- Succession planning: Ensuring sufficient numbers of people are ready to take on new roles as others leave, retire, or are promoted
This model is helpful in industries that have high turnover or require constant leadership development. Think retail, hospitality, or healthcare, where employee movement is frequent.
4. The Optimization Model
The optimization model finds the most efficient way to allocate workforce resources across the organization to achieve specific business objectives. It uses mathematical algorithms and data models to discover the implications of different scenarios.
- Optimization techniques: Linear programming, simulations, cost minimization, and productivity maximization are used to determine the most efficient resource allocation.
- Cost efficiency: Incorporating budget constraints, it aims to achieve the best possible staffing solution at the lowest cost.
Any companies looking to optimize labor costs while ensuring sufficient staffing levels, such as in logistics companies, call centers, or manufacturing plants where workforce allocation directly impacts efficiency and cost, can make good use of this model.
The role of technology in workforce planning
Future-proof your organization by implementing advanced tools and data analytics to streamline workforce planning processes. Technology can mitigate risk, reduce human bias, and increase cost efficiencies by improving decision-making. It allows an organization to quickly adapt to changing business environments with agility and efficiency.
How technology is changing workforce planning
Lisa Harrison, an associate client partner at Korn Ferry, states, “What we’re seeing in the market is most companies lack the internal analytic capability.”
Innovations like automation, AI, and predictive analytics empower organizations with powerful tools that can analyze large amounts of workforce data, forecast future staffing needs, and optimize their workforce strategies.
You could use AI to predict talent gaps by analyzing historical data and market trends, enabling you to proactively address staffing needs before they arise. Or why not help your HR leaders make more accurate decisions by forecasting turnover rates, hiring requirements, and skill shortages?
A shift to technology can transform workforce management from a reactive to a proactive function, making organizations more agile and responsive to evolving business needs.
The use of HR software in workforce planning
Modern workforce strategies consolidate employee data through technology, improving HR analytics. Cutting-edge software can generate actionable insights for strategic decision-making. Integrating that with talent management programs, you can now monitor performance, track skills development, and align a workforce planning strategy with your broader business goals.
Workhuman offers a suite of tools designed to enhance operational workforce planning and employee engagement. The Workhuman Cloud platform helps organizations leverage data-driven insights, employee feedback, and recognition to create a more engaged and high-performing workforce.
- Real-time feedback and recognition: This allows employees to receive timely feedback, supporting their professional growth and informing workforce planning decisions.
- Data-driven insights: Workhuman’s analytics tools help businesses track metrics such as employee engagement, performance, and retention, ensuring decisions are backed by solid data.
- Employee engagement: The platform enhances employee satisfaction through recognition, boosting retention and productivity.
Workhuman’s solutions highlight how HR technology can optimize workforce management while fostering a positive organizational culture.
Benefits and challenges of using technology in workforce planning
For planning workforce strategies, as in just about every aspect of business, new technology has a lot to bring to the table:
- Advanced analytics provide better data, leading to more informed decisions about hiring, talent development, and succession planning.
- Automation streamlines processes so that recruitment, onboarding, and performance evaluations become simpler, reducing administrative workload and improving time-to-hire.
- Technology enables scaling as workforces and the strategies for managing them grow.
- Managers and leaders can use tools to improve collaboration and align workforce strategies, track progress, and share insights.
Technology does, however, present challenges:
- Data security: Storage of sensitive employee data raises concerns. Cybersecurity and data privacy are hot tickets, and companies must comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA to protect this information.
- Integration issues: Integrating new technologies with legacy systems can be complex, leading to inefficiencies and inconsistent data.
- Cost of implementation: Tech can be expensive, particularly for smaller businesses, with high initial costs for licensing, training, and support.
- Adoption resistance: Unfamiliar technology can be met with employee resistance that may require proper training and change management processes to overcome.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of advancing business with technology for workforce planning far outweigh the drawbacks.
Conclusion
Strategic workforce planning is as much about anticipating tomorrow's needs as it is about overcoming today's challenges. Going further than just filling positions, strategic planning makes sure that the right people are embedded in the business by identifying critical roles early on and nurturing internal talent.
Crucially, you must assess current capabilities, predict future staffing requirements, and identify talent gaps. Remember that planning isn’t a one-off task. Keep refining your strategy as business goals evolve to make sure your workforce is ready to match and exceed all of your organizational needs.