AI in Business Intelligence: Unlocking the Power of Data-Driven Decision Making
Harvard Business Review's 2023 survey, Transforming Data into Business Value through Analytics and AI, underscores the enormous potential of data to drive business growth. It found that organizations leveraging analytics to guide decisions consistently outperform those that don’t - particularly in key areas such as customer retention, employee satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
There are multiple ways for companies to use data as a tool to optimize performance, boost profits, and achieve business goals. Business Intelligence (BI) applies advanced analytics to historical data to predict trends and generate insights, while Artificial Intelligence (AI) relies on machine learning and other cutting-edge technologies to streamline workflows and enhance decision-making.
Developments in both fields are bringing AI and business intelligence together to offer companies even more powerful tools for transforming data into successful business strategies.
What is Business Intelligence (BI)?
Business intelligence refers to technological processes, systems, and methods for collecting and analyzing data to generate insights that improve organizational decision-making and optimize business strategies. By leveraging a range of BI tools, businesses can analyze many types of data, such as:
- Historical and current organizational data
- In-house data
- Third-party data
- Semi-structured data
- Unstructured data
BI enables organizations to leverage data analytics to develop a snapshot of performance, understand the factors that have influenced performance, and make data-informed determinations about actions necessary to maintain or improve outcomes. In other words, BI helps businesses understand why certain events happened, such as an uptick in sales or a sudden drop in conversions or impressions.
To measure performance, BI relies on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). These specific, data-derived metrics enable management teams to make quantitative assessments of the success of people, actions, and strategies in achieving predefined business goals. They clarify relevant business trends and spotlight strategies that are working and areas where improvements are necessary.
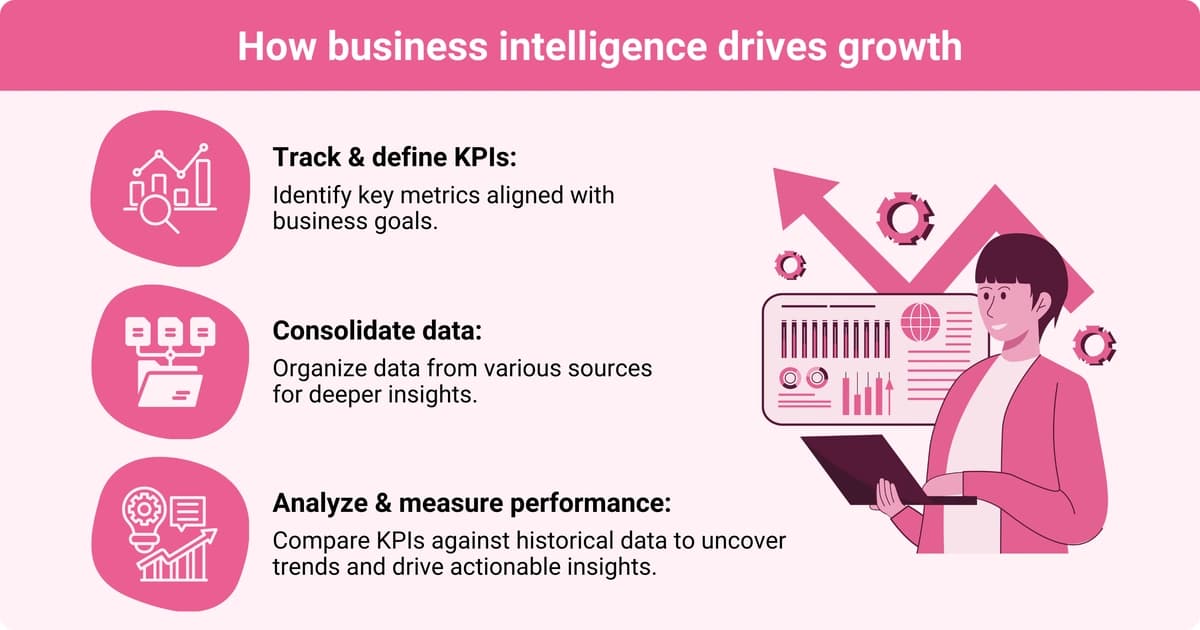
Through business intelligence, businesses can:
- Define and track KPIs: BI platforms help businesses determine which KPIs are most relevant to specific business objectives and track and measure KPIs to monitor progress.
- Gather and consolidate data: BI systems provide businesses with a comprehensive understanding of organizational performance by harvesting data from various sources, organizing it, and preparing it to be analyzed.
- Analyze data and measure performance: BI systems compare KPIs against historical business data, competitor data, and market benchmarks to identify performance trends and link factors to business outcomes. BI tools for data reporting and visualization make raw data clear and understandable to stakeholders so they can translate it into actionable insights that drive growth.
Common BI tools and platforms
A range of available tools and platforms makes BI more accessible to organizations. In general, BI platforms organize all of a business’s data in a single location and make that data clear and understandable so that decision-makers can leverage it to develop strategies that improve business performance.
It’s important to understand that BI platforms are separate from other types of analytics software. They share commonalities, providing data cleaning, analysis, and forecasting. But BI platforms go beyond mere collection and analysis.
They use tools and functions that allow businesses to monitor marketing campaigns and analyze results, automate data reporting and report distribution, track and visualize inventory, and forecast and visualize sales and profits in real time.
Depending on the specific platform, BI tools may feature a range of additional functionalities for using data. For example, the top BI platforms integrate with cloud-computing services from third parties to streamline business processes.
Although complete functionality differs from platform to platform, a useful BI platform offers a combination of a few basic tools:
- Customizable dashboards
- Report scheduling
- Enhanced data-mining
- KPI performance tracking
- Natural language processing (NLP)
- Data quality management
BI platforms themselves may be commercially produced or built on open-source software. When it comes to choosing a platform, consider the functionalities and tools on offer and pick the platform with capabilities that are aligned with your business goals.
That said, most organizations stand to gain from a BI platform that includes features like dynamic dashboards, intuitive analytics visualizations, and transparent pricing models.
How BI tools help organizations make sense of data
Business intelligence tools and platforms help organizations make sense of data by translating it into insights that propel decision-making and lead to more satisfactory business outcomes. Doing so requires a combination of functionalities for collecting data, data analysis and visualization, and data reporting. In general, the process works like this:
- Data collection and integration: Data is collected from various sources. Those sources may be an organization's customer relations management system (CRM), spreadsheets, databases, or other systems. The data is then put through a cleaning process, which corrects errors and removes information that is incomplete or irrelevant.
- Data analysis and translation: BI platforms can analyze data according to several techniques, including data mining, predicting analysis, and statistical analysis. The platform scours the data to identify trends, patterns, and inconsistencies.
- Data visualization and reporting: After analysis, BI platforms present the findings on dashboards in the form of reports and visualizations, such as charts and graphs, that make the data more understandable.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
In a broad sense, artificial intelligence refers to computers and other machines that can perform tasks, such as learning, reasoning, and other actions, that have traditionally required human intelligence. In other words, AI technology enables computers to adapt to changing inputs and learn from past inputs or experiences like humans do.
Mimicking human cognition in computers involves a range of advanced computational techniques, including:
- Machine Learning (ML): This refers to computer systems that are able to “learn” via statistical modeling and algorithms, as opposed to responding to explicit instructions like code. Essentially, machine learning enables computers to make inferences by extrapolating patterns from data.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP is a field of machine learning that involves programming computers to understand and process human language. Generative AI systems combine linguistics and artificial intelligence to enable computers to respond to written or spoken language in a way that’s similar to humans.

AI has a number of specific applications with regard to business. Businesses can use computer systems that simulate human intelligence to perform decision-making and problem-solving functions and to predict future trends about specific business actions.
In other words, AI takes traditional data analytics a step further. Instead of merely analyzing organizational data, businesses can use AI tools for advanced predictive analytics, the process of using historical data to forecast future outcomes or trends. Essentially, it enables businesses to propose scenarios and predict what is likely to happen based on past patterns.
Likewise, AI enables businesses to marshal the power of data to make informed decisions about business processes. This is known as prescriptive analytics, the practice of using data-driven insights to determine the steps that should be taken to accomplish a specific outcome.
Core capabilities of AI
AI poses a range of unique and valuable benefits to organizations that integrate these technologies into their business processes. The field of AI is rapidly advancing, but businesses of all kinds are already using many core AI capabilities to boost productivity and improve performance, including:
- Task automation: One of the most common uses of AI technology in business is automation. Many business tasks that are essential for operations are also time-consuming, repetitive, and low-value. AI automation allows businesses to reassign those tasks to computers, which can perform them much more quickly and with far fewer errors compared to humans.
For example, in marketing, AI automation streamlines key tasks like audience segmentation.
- Trend identification and prediction making: AI systems can analyze large amounts of raw data according to preselected KPIs to identify trends. The technology can then make data-informed predictions about the results that are likely to stem from specific strategies.
- Enhanced decision-making: In addition to analyzing datasets at a pace that far surpasses human capabilities, AI technology can do so in real time. This enables organizations to apply AI-driven insights to business processes based on the most current, up-to-date information available.
Limitations of AI
Although AI is transforming the business landscape in many positive ways, the technology is not without its limitations. One key limitation is that to deliver quality insights and recommendations, AI requires quality data. Inaccuracies in data, such as biases or missing data, lead to insights that may be inaccurate.
Another limitation is that AI relies on complex algorithms. On the one hand, this complexity improves AI by enabling it to perform tasks of greater complexity and process larger and larger datasets. However, that complexity poses problems when it comes to:
- Human interpretation: The humans who use AI technology may struggle to understand and interpret the complex algorithms AI runs on. This can prevent decision-makers from fully understanding why a certain recommendation is being suggested or why a certain insight holds true. It may also complicate the ability of IT staff to debug machines running AI technology.
- Computational capabilities: The resources required to run complex algorithms are another barrier. Organizations may lack the time, energy resources, and even the hardware required.
- Biased outcomes: AI systems are trained on data that may contain biases. When that happens, those biases often reappear in the algorithms themselves, which can lead to unfair and even discriminatory outcomes.
Finally, integrating AI technology into business operations is a large investment. First, there's the costliness of AI integration. However, that is often balanced by the increase in productivity and boost in profits that comes from time savings and procedural optimization.
Second, there's the resource-intensive aspect. Integrating AI may require the installation of dedicated hardware, migration to cloud-based services, and a range of systems for storing and managing data. Additionally, businesses need to invest in software to support AI infrastructure, including machine learning libraries and programming languages.
Beyond those resources, AI requires advanced technical expertise. Organizations may need to staff professionals with backgrounds in AI engineering, data science, and machine learning, as well as analysts who are able to correlate business needs with AI solutions.
Depending on the scale of AI integration, businesses may also need to invest in training programs that reskill employees in areas related to AI.
Common differences between BI and AI
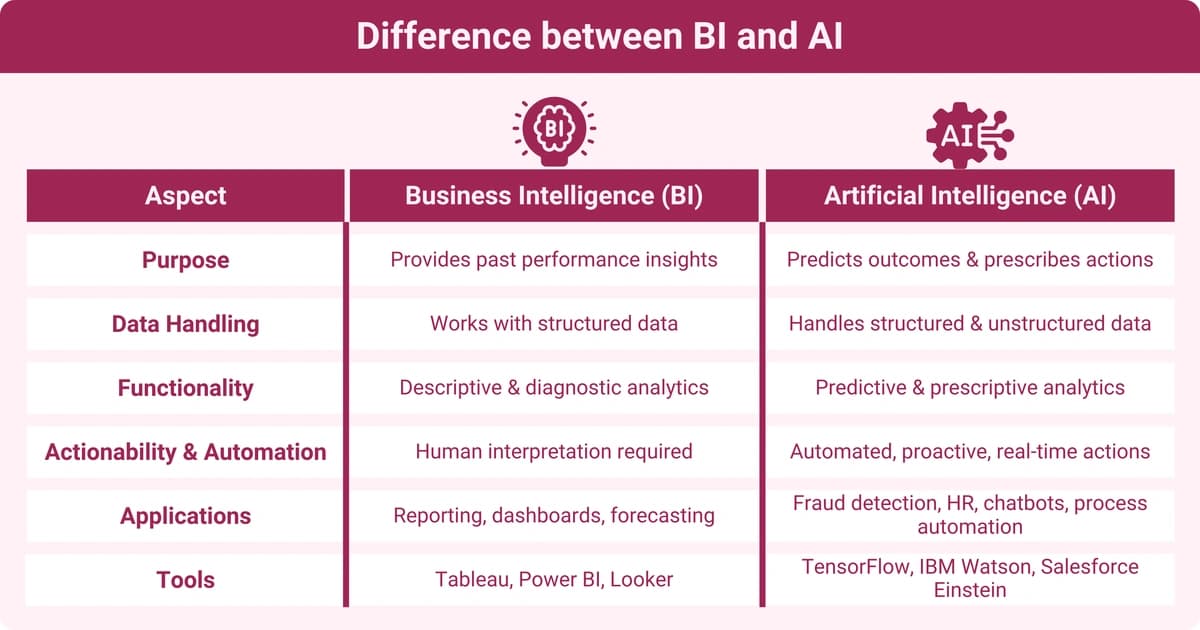
The difference between business intelligence and artificial intelligence lies in their respective purposes, functionalities, and how they work with data. BI and AI are often complementary and can be used together. However, their roles and capabilities differ significantly.
Data handling
Among the largest differences between AI and BI have to do with how each handles data. BI works with structured data that has been organized according to a predefined format, which is easier for computers to process and analyze.
Business intelligence tools draw structured data from various sources, including spreadsheets, software systems, and databases, and then transform it into reports and visualizations.
AI works a little differently. In addition to structured data, AI can also manage unstructured data, or data that lacks consistent organization or form. Unstructured data can be text documents, images, and even video. AI recognizes patterns and generates insights from both structured and unstructured data through the use of algorithms and computer modeling that enable it to learn dynamically.
Functionality
There are further differences between AI and BI with regard to the analytic practices that each uses to make sense of organizational data. Business intelligence generally focuses on two analytic techniques to provide performance snapshots and produce insights:
- Descriptive analytics: Descriptive analytics describes events and outcomes by analyzing historical data. In other words, it helps businesses make decisions based on an improved understanding of things that have happened in the past.
- Diagnostic analytics: Like descriptive analytics, diagnostic analytics uses past data to derive insights. However, it goes beyond describing what happened and uses various techniques, from data mining to correlation identification, to identify patterns and relationships that are hidden deep within datasets.
AI, on the other hand, is better at using predictive and prescriptive analytics. Predictive analytics answers questions about events that are likely to transpire as a result of certain actions. Prescriptive analytics is about making recommendations for actions that an organization should take in order to achieve a certain outcome.
For example, businesses often want to predict customer churn, the rate at which customers stop doing business with an organization. AI can use predictive and prescriptive analysis to scour historical data to determine what events resulted in lost customers and then recommend strategies that businesses can implement to boost retention.
Furthermore, AI automates processes for data collection and analysis so that an organization can refine and adapt its business processes in response to fluctuations in data.
Actionability and automation
BI tools enable businesses to analyze data from events that have already occurred. However, they require humans to interpret the information on BI dashboards and to put those interpretations into action.
AI takes a more proactive approach. AI has the capability to highlight trends and forecast outcomes, in addition to analyzing past events. Additionally, AI automation can effectively take action in response to data without human intervention, beyond initially scheduling the automation.
For example, consider AI chatbots. These work in real-time to analyze data, in the form of a conversation with a human user, and respond appropriately.
AI chatbots handle these interactions without the assistance of a human, simply by analyzing in-chat data according to the algorithms and data they were trained on. Similarly, businesses can automate decision-making with AI based on algorithms and predictive models.
Applications
There are further differences between the specific applications that BI and AI provide.
BI applications
Business intelligence applications are aimed at enabling businesses to optimize performance through data-driven decision-making. Their functionality supports those aims with tools for collecting, analyzing, and storing unstructured data.
Common tasks these applications perform include:
- Data mining: BI platforms typically include applications for tracking metrics, KPIs, and other historical data. Then, by applying statistical analysis and often machine learning, they identify patterns in large datasets to generate insights.
- Forecasting: Another valuable function of BI platforms, forecasting, is accomplished with applications that engage market research, predictive analytics, and other advanced analytics techniques on historical data. This enables businesses to make informed predictions about future events across departments.
- Reporting: Functionality that supports reporting can vary from platform to platform, but commonly includes features for querying, filtering, integrating, and warehousing data. Platforms may also offer automated reporting and options for customizing report formats.
Visualization is a key component of making raw data intelligible so that insights can be extracted and applied to operations. The best BI applications feature customizable dashboards, allowing users to generate a range of visualizations that best serve their specific goals.
These include various types of charts, such as bar charts, pie charts, histograms, line graphs and scatter plots, and mapping tools like heatmaps and treemaps.
BI software dashboards may offer further customization options, from color palettes and font types to widgets and dashboard themes.
AI applications
AI systems like Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud AI, and the open-source platform Prophet leverage predictive analytics and AI automation to streamline workflows and optimize performance for businesses across industries. For example, in finance, these applications help improve investment decisions, detect and prevent fraud, and mitigate risks.
Likewise, AI-enabled platforms help human resources professionals manage diverse challenges. AI in recruitment examples show how AI can save time and improve candidate screening. Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives benefit from how DEI and AI can synergize to identify pay discrepancies, encourage inclusive language, and improve accessibility.
Workhuman iQ features powerful tools that enhance productivity, boost retention, and increase ROIs. Through proprietary algorithms, specialized dashboards, and other tools, Workhuman iQ makes real-time employee data immediately accessible and delivers unique insights into company culture, DEI, and skills, optimizing:
- Employee recognition programs
- Mentorship matching
- Training
- Succession planning
Workhuman iQ can transform your understanding of the employee experience with AI-powered social analytics to unlock data-driven strategy. It's the kind of intel you’ve always wanted, delivered in a way that anyone can use.
How to use AI in business intelligence
At the intersection of business intelligence and artificial intelligence are powerful tools that can transform businesses of all kinds. Applications of AI in business leverage powerful technologies like machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing (NLP). These tools enable real-time data analysis, enhance insight extraction, and improve predictions.
More and more BI tools are incorporating AI power into their platforms, including:
- Qlick: An AI-driven Insight Advisor leverages NLP technology that delivers insights, predictive analytic reports, and data summaries in response to user questions.
- Domo.AI: The Domo platform integrates AI in various ways. AI Chat enables users to ask specific data questions of AI chatbots and glean deeper, more actionable insights. AI Agents enhance customer experiences in retail with targeted recommendations and other personalization techniques. The platform also offers optimization tools like task automation and real-time inventory management.
- Tableau: Tableau’s AI tools are aimed at expediting the data analytics process and improving decision-making and the quality of insight extraction. Some of the features it offers include AI-generated prompts for calculations and visualizations, one-click reporting, and oral calculation instruction.
Conclusion
Through complex data analytics processes, BI tools gather, parse, and interpret large datasets. Then the data is transformed into user-led visualizations on customized dashboards.
AI systems can streamline workflows, improve decision-making, and alleviate pain points across nearly every aspect of business. Automation capabilities and technologies like machine learning, deep learning, and NLP enable seamless human and AI collaboration.
On their own, business intelligence and AI are both powerful resources for optimizing operations in businesses of all kinds. But together, their power increases exponentially, allowing for faster insight generation, real-time functionality, and other enhancements.
Now that you have a deeper understanding of the BI/AI landscape and how business intelligence driven by AI can take companies to the next level, it’s time to start thinking of how you can implement these tools into your operational strategy.
About the author
Anna Picagli
As an RYT500 yoga instructor and a Reiki Master Teacher, Anna is an advocate for holistic wellness, especially within the workplace. She’s extremely passionate about the brain-body connection and exploring how mental and physical wellness intersect.
Anna has experienced firsthand how chronic stress, overworking, poor management, and other organizational issues can lead to extreme burnout. Knowing the impact that a toxic work environment can have on a person’s body, psyche, and general sense of well-being, she now works to direct others away from facing the same fate.
As Workhuman’s Senior Content Specialist, Anna is a regular contributor to Workhuman iQ reports and aims to create resources that company leaders can reference to help improve their culture and empower their employees, creating healthier workplaces for everyone.
In her free time, she’s an avid solo traveler, a voracious reader, and a seasoned home chef. You can learn more about Anna’s work on LinkedIn or through the Yoga Alliance.